WiMax (Wireless Interoperability for microwave access) is a wireless digital communication system based on IEEE 802.16 standards. It can be used for transmitting data from a fixed station as well as a mobile station. It can provide wireless access upto 50 km for fixed stations and 15 km for the mobile ones.
Among the main uses of WiMax comes the internet connectivity for laptops. In a radius of upto 10 km WiMax can give access rates of upto 40Mbps per channel. In India(a south asian fast developing economy), WiMax network is being setup in Chennai, a city in south of India. This technology if spreads out to the entire country can benefit the 1 billion citizens of India, especially the villages of India where still for many using internet remains a dream.
Associated Links :
Thursday, October 4, 2007
Monday, October 1, 2007
CDMA or GSM
In the present day scenario the GSM (Global System for mobile communication) is dominating in most parts of the world, but rapidly the CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) is taking over it because of the additional advantages it provides.
In CDMA there is no division of frequency band unlike GSM which assigns a specific frequency to each user. Each user in GSM is identified using the SIM(Subscriber Identity module) card which stores the service subscriber key used to identify the user.

On the left is shown a CDMA phone by Tata Indicom.
CDMA employs spread spectrum technology in which the energy generated in a particular bandwidth is spread in the frequency band. This frequency band is used for all the users. It provides better bandwidth for the voice and data transmission over the network and hence increases the number of people that can be connected at any given time. This means using it you will hear less of those irritating("Network is currently busy") messages. Surely CDMA provides high speed services.
But inspite of all these benefits of CDMA we cannot forget the advantage given to SIM card owners to easily change their mobile phones.
In CDMA there is no division of frequency band unlike GSM which assigns a specific frequency to each user. Each user in GSM is identified using the SIM(Subscriber Identity module) card which stores the service subscriber key used to identify the user.

On the left is shown a CDMA phone by Tata Indicom.
CDMA employs spread spectrum technology in which the energy generated in a particular bandwidth is spread in the frequency band. This frequency band is used for all the users. It provides better bandwidth for the voice and data transmission over the network and hence increases the number of people that can be connected at any given time. This means using it you will hear less of those irritating("Network is currently busy") messages. Surely CDMA provides high speed services.
But inspite of all these benefits of CDMA we cannot forget the advantage given to SIM card owners to easily change their mobile phones.
Friday, September 28, 2007
Removing the hand icon displayed below shared drives
Whenever we share any of our harddisk drives a hand icon appears below that drive. Surely, a nice way to show that it is shared, but when all your drives are shared, the same hand starts annoying us. In order to get rid of this hand we have to perform a registry tweak.
Open regedit ( Go to start>Run and type in regedit) .
Open regedit ( Go to start>Run and type in regedit) .
- Browse to the location HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT>Network>Sharing Handler.
- Open the default icon by double clicking it.
- In the value data textbox the default value is ntshrui.dll.
- Erase this value to leave the space blank.
- Restart your PC and see the change in the icon of your shared drives.
Thursday, September 20, 2007
Disabling Windows Error Reporting
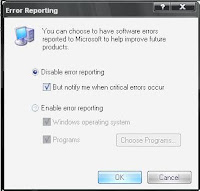
It's pretty much frustrating when windows prompts you to report the errors to the microsoft website. You can stop this reporting if you like by following some simple steps.
Well now you can fell free of those irritating error reporting messages and enjoy your work on the PC.
- Open the control panel
- Double click on the System icon
- Click on the Advanced tab
- Click on the button named "Error Reporting"
- Now on the window that appears click disable error reporting as shown.

Well now you can fell free of those irritating error reporting messages and enjoy your work on the PC.
Sunday, September 16, 2007
Renaming the Recycle Bin
When it comes to playing with your system settings, there is no better place than regedit to get your hands dirty on. Regedit the short for registry editor allows us to make changes in the windows settings pretty easily. Changes like changing the boot up screen, wallpapers, security related issues can easily be tackled with through the registry.
When you right click on the recycle bin unlike other icons, the rename option is not displayed in the pop-up menu. But this doesn't mean it can;t be changed. Well now it's time to open up regedit. For that go to the Start>run. Then type regedit. You will be presented with a screen as shown below :
Now go to the location "HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT/CLSID/{645FF040-5081-101B-9F08-00AA002F954E/ShellFolder/}" by expanding the '+' signs.
Once you reach there double click the "Attributes" icon.
Then change the value data from "40 01 00 20" to "50 01 00 20".
Now double click "CallForAttributes" icon and change the value data to 0.
Rejoice! Now you can jump back to your desktop and right click the recycle bin to see the rename option. Click it and name the recycle bin to whatever you want.
Some tweaks you can perform (Always remember to create a backup of your registry before performing any of the registry tweaks) :
When you right click on the recycle bin unlike other icons, the rename option is not displayed in the pop-up menu. But this doesn't mean it can;t be changed. Well now it's time to open up regedit. For that go to the Start>run. Then type regedit. You will be presented with a screen as shown below :

Now go to the location "HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT/CLSID/{645FF040-5081-101B-9F08-00AA002F954E/ShellFolder/}" by expanding the '+' signs.
Once you reach there double click the "Attributes" icon.
Then change the value data from "40 01 00 20" to "50 01 00 20".
Now double click "CallForAttributes" icon and change the value data to 0.
Rejoice! Now you can jump back to your desktop and right click the recycle bin to see the rename option. Click it and name the recycle bin to whatever you want.
Some tweaks you can perform (Always remember to create a backup of your registry before performing any of the registry tweaks) :
Wednesday, September 12, 2007
Auto shut down of the computer for firefox download
After working for hours to find the correct matter to download, surely one does get exhausted and does need some rest. But after all this if you have to wait for the download to finish, frustration is an obvious outcome.
For all you guys who work on firefox most of the time, there is a Add-on provided by firefox which allows you to turn off your computer once the list of download items finishes. It adds an icon to the status bar and the download manager, which enables you to automatically shut your computer down once the download has finished. To download this add-on click here.
For all you guys who work on firefox most of the time, there is a Add-on provided by firefox which allows you to turn off your computer once the list of download items finishes. It adds an icon to the status bar and the download manager, which enables you to automatically shut your computer down once the download has finished. To download this add-on click here.
Sunday, September 9, 2007
Creating a Bootable Pen Drive
All of us must have encountered the situation where our very own PC refuses to boot whatever the problem may be. It is here that a USB drive containing bootable XP comes in handy. You can install a bootable XP on to the pen drive along with the safety tools such as antivirus etc. to fix the problem.
But this cool way might not shine the light equally on everyone. In order to boot from a flash drive your system should be only around two years old. An alternative to this is that you upgrade your BIOS. Also the flash drive you use should be of a minimum of 256 Mb size to hold windows XP. Also a maximum size of 2GB is permissible.
So now you have the pendrive and an approprite BIOS. So get started with creating a bootable pen drive. For that you need to have a USB Disk storage format tool which is available for free. Now you can start formatting your pen drive. Then to make it bootable copy the following files on to the pen drive : Boot.ini, NTLDR, and NTDETECT from root directory of the boot drive.
Now you will be needing a software named BartPE that helps you install windows on a minimal space. After you have downloaded it follow the steps to copy the Windows files.
After you are done with all this you are having your very own flash drive ready to boot your Windows XP2.
Associated links :
But this cool way might not shine the light equally on everyone. In order to boot from a flash drive your system should be only around two years old. An alternative to this is that you upgrade your BIOS. Also the flash drive you use should be of a minimum of 256 Mb size to hold windows XP. Also a maximum size of 2GB is permissible.
So now you have the pendrive and an approprite BIOS. So get started with creating a bootable pen drive. For that you need to have a USB Disk storage format tool which is available for free. Now you can start formatting your pen drive. Then to make it bootable copy the following files on to the pen drive : Boot.ini, NTLDR, and NTDETECT from root directory of the boot drive.
Now you will be needing a software named BartPE that helps you install windows on a minimal space. After you have downloaded it follow the steps to copy the Windows files.
After you are done with all this you are having your very own flash drive ready to boot your Windows XP2.
Associated links :
Thursday, September 6, 2007
NTFS (New Technology File System)
Whenever you are formatting your harddisk, the option for either a NTFS or a FAT file system pops up. Fine you know NTFS is new and better but how.
A file system is a part of the operating system that determines how files are named, stored and organized on a volume. FAT (File allocation table ) was the standard file system developed by microsoft for the MS-DOS. This was used in all the windows till the Windows ME. Then came the NTFS (New Technology File System) which almost replaced the FAT file allocation.
The NTFS allows greater reliability, security, greater volume size etc. In NTFS all the characteristics of the file (like filename, date of creation) are stored as metadata. NTFS utilizes the power of B+ trees to index file system data. The master file table is used to store the metadata about every file present on the volume. In this system greater security is provided as we can restrict access of files to authorized users.
These features of NTFS sure does give them a reason to be chosen while opting for the type of file system for formatting.
Associated topics :
A file system is a part of the operating system that determines how files are named, stored and organized on a volume. FAT (File allocation table ) was the standard file system developed by microsoft for the MS-DOS. This was used in all the windows till the Windows ME. Then came the NTFS (New Technology File System) which almost replaced the FAT file allocation.
The NTFS allows greater reliability, security, greater volume size etc. In NTFS all the characteristics of the file (like filename, date of creation) are stored as metadata. NTFS utilizes the power of B+ trees to index file system data. The master file table is used to store the metadata about every file present on the volume. In this system greater security is provided as we can restrict access of files to authorized users.
These features of NTFS sure does give them a reason to be chosen while opting for the type of file system for formatting.
Associated topics :
Monday, September 3, 2007
Rules for Creating a Relational DBMS
So all you programmer's out there think just implementing a database in the form of tables makes your database a relational Database (RDBMS). Well then E.F. Codd challanges this thought of yours. Edgar F. Codd was a british computer scientist who has given a set of 12 rules necessary for creating a relational database. Most of the database management systems like Oracle, SQL server etc. incorporate most of these rules. The rules are :
(1)Information Rule:
All information in a relational database including table names,column names are
represented explicitly by values in tables. Knowledge of only one language is necessary to
access all data such as description of the table and attribute definitions ,integrity
constraints,action to be taken when constraints are voilated,and security information.
(2)Guaranted Access Rule:
Every pieceof data in the relational database,can be accessed by using a
combination of a table name, a primary key value that identifies the row and a column
that identifies the cell.The benefit of this is that user productivity is improved
since there is no need to resort to using physical pointers addresses.Provides
data independence.
(3)Systematic treatment of Nulls Rule:
The RDBMS handles that have unknown on inapplicable values in a predefined fashion.
RDBMS distinguishes between zeros,blanks and nulls in records and handles such values in
a consistent manner that produces correct answers,comparisions and calculations.
(4)Active On-Line Catalog Based on the Relational Model.
THe description of a database and its contents are database tables and therefore
can be queries online via the data language.The DBA's productivity is improved since
changes and additionsto the catalog can be done with the same commands that are
used to access any other table.All queries and reports can be done as with other tables.
(5)Comprehensive Data Sublanguage Rule:
A RDBMS may support several languages,but atleast one of them allows the user to do all
of the following:define tables view,query and update data ,set integrity constraints,
set authorization,and define transactions.
(6)View Updating Rule:
Any view that is theoretically updatable,if changes can be made to the tables that
effect the desired changes in the view.Data consistency is ensured since changes
in the underlying tables are transmittedto the view they support.Logical data
independence reduces maintenance cost.
(7)High Level Inserts,Update and Delete:
THe RDBMS supports insertion,updation and deletion at a table level.With this the
RDBMS can improveperformance by optimizing the path to be taken to execute the action
Ease of use improved since commands act on set of records.
(8)Physical data Independence :
The execution of adhoc requests and application programs is not affected by changes
in the physical data access and storage methods.Database administrators can make
the changes to physical acccess and storage methods ,which improve performance
but do not changes in the application programs or adhoc requests.This reduces
maintenance costs.
(9)Logical data Independence:
Logical changes in tables and view such asadding/deleting columns or changing
field lenghts do not necessitate modifications in application programs or in the
format of adhoc requests.
(10)Integrity Independance:
Like table/view definitions ,integrity constraints are atored in the
on-line catalog and therefore can be changed without necessitating changes
in application programs or in the format of adhoc requests .
The following two integrity constraints must be supported.
(a)Entity Integrity:
No component of primary key is allowed to have anull value.
(b)Referential integrity:
For each distinct non-null foreign key value in a relationaldatabase,
there must exist a matching primary key from the same range of data value.
(11)Distribution Independence:
Application programs and adhoc requests are not affected by changes
in the distribution of the physical data.
(12)Nonsubversion Rule:
If the RDBMS has a language change that accesses the information
of a record at a time,this language cannot be used to by-pass the
integrity constraints.Inoreder to adhere to this rule the RDBMS must have an
active catalog that containsthe constraints must have a logical data independence.
(1)Information Rule:
All information in a relational database including table names,column names are
represented explicitly by values in tables. Knowledge of only one language is necessary to
access all data such as description of the table and attribute definitions ,integrity
constraints,action to be taken when constraints are voilated,and security information.
(2)Guaranted Access Rule:
Every pieceof data in the relational database,can be accessed by using a
combination of a table name, a primary key value that identifies the row and a column
that identifies the cell.The benefit of this is that user productivity is improved
since there is no need to resort to using physical pointers addresses.Provides
data independence.
(3)Systematic treatment of Nulls Rule:
The RDBMS handles that have unknown on inapplicable values in a predefined fashion.
RDBMS distinguishes between zeros,blanks and nulls in records and handles such values in
a consistent manner that produces correct answers,comparisions and calculations.
(4)Active On-Line Catalog Based on the Relational Model.
THe description of a database and its contents are database tables and therefore
can be queries online via the data language.The DBA's productivity is improved since
changes and additionsto the catalog can be done with the same commands that are
used to access any other table.All queries and reports can be done as with other tables.
(5)Comprehensive Data Sublanguage Rule:
A RDBMS may support several languages,but atleast one of them allows the user to do all
of the following:define tables view,query and update data ,set integrity constraints,
set authorization,and define transactions.
(6)View Updating Rule:
Any view that is theoretically updatable,if changes can be made to the tables that
effect the desired changes in the view.Data consistency is ensured since changes
in the underlying tables are transmittedto the view they support.Logical data
independence reduces maintenance cost.
(7)High Level Inserts,Update and Delete:
THe RDBMS supports insertion,updation and deletion at a table level.With this the
RDBMS can improveperformance by optimizing the path to be taken to execute the action
Ease of use improved since commands act on set of records.
(8)Physical data Independence :
The execution of adhoc requests and application programs is not affected by changes
in the physical data access and storage methods.Database administrators can make
the changes to physical acccess and storage methods ,which improve performance
but do not changes in the application programs or adhoc requests.This reduces
maintenance costs.
(9)Logical data Independence:
Logical changes in tables and view such asadding/deleting columns or changing
field lenghts do not necessitate modifications in application programs or in the
format of adhoc requests.
(10)Integrity Independance:
Like table/view definitions ,integrity constraints are atored in the
on-line catalog and therefore can be changed without necessitating changes
in application programs or in the format of adhoc requests .
The following two integrity constraints must be supported.
(a)Entity Integrity:
No component of primary key is allowed to have anull value.
(b)Referential integrity:
For each distinct non-null foreign key value in a relationaldatabase,
there must exist a matching primary key from the same range of data value.
(11)Distribution Independence:
Application programs and adhoc requests are not affected by changes
in the distribution of the physical data.
(12)Nonsubversion Rule:
If the RDBMS has a language change that accesses the information
of a record at a time,this language cannot be used to by-pass the
integrity constraints.Inoreder to adhere to this rule the RDBMS must have an
active catalog that containsthe constraints must have a logical data independence.
Thursday, August 30, 2007
Minicomputers
Minicomputer is a computer which is having a size in between the mainframe computers and the microcomputers.
These minicomputers behave as a stand-alone computer with a number of terminals attached to it. They were small computers ( compared to the then existing mainframe computers ). This had been achieved with the introduction of transistors and core memory technologies.
The magnetic core memory or the ferrite core memory is a kind of computer memory. It stores information in magnetic ceramic rings which can store a bit(0 or 1) of information.

These rings are arranged in a grid form as shown.
But the minicomputers still had few drawbacks like large size, expensive to buy which gave way to the invention of the microcomputers which is visible in almost every household now a days.

These minicomputers behave as a stand-alone computer with a number of terminals attached to it. They were small computers ( compared to the then existing mainframe computers ). This had been achieved with the introduction of transistors and core memory technologies.
The magnetic core memory or the ferrite core memory is a kind of computer memory. It stores information in magnetic ceramic rings which can store a bit(0 or 1) of information.

These rings are arranged in a grid form as shown.
But the minicomputers still had few drawbacks like large size, expensive to buy which gave way to the invention of the microcomputers which is visible in almost every household now a days.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)


